Feb 1, 2025
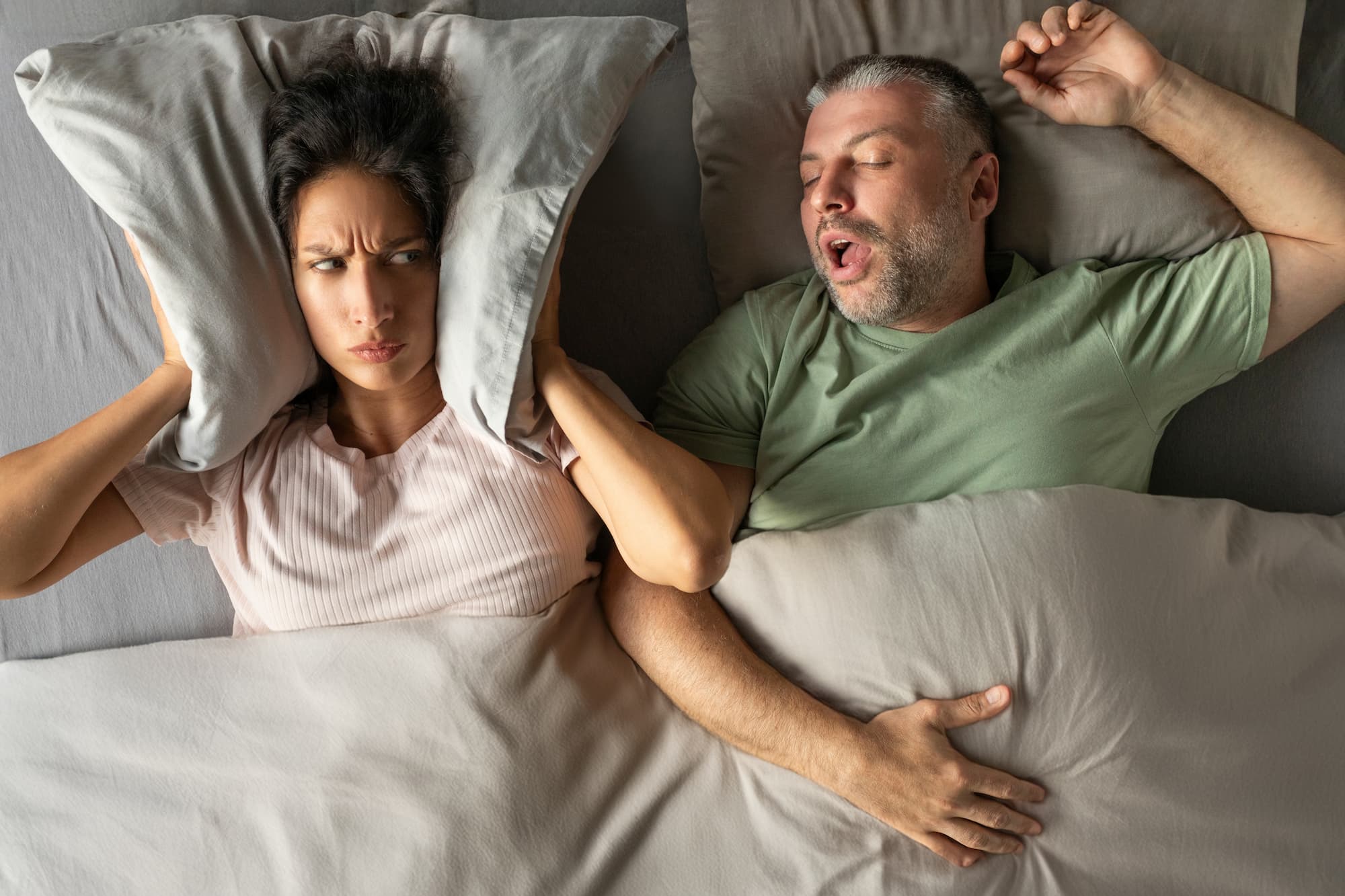
Snoring is a common nighttime phenomenon that many encounter, whether it is from ourselves, a partner, or family members. While some may see it as a harmless noise, for others, it can be a loud and disturbing noise that distracts their sleep, strains relationships or triggers potential health issues.
It is a rhythmic rumbling, gasping, or snorting sound arising from obstructed breathing while asleep. On average, about 25-50% of the adult population snore regularly. It is not limited to a specific age group—it can affect anyone, from children and teenagers to adults and the elderly.
This article will try to reflect expert insights on why people snore when sleeping, what causes, health effects, when to see a doctor, treatment options, and other lifestyle changes that can help manage this condition.
Why Do People Snore?
Snoring happens when you’re asleep and your pharynx, a part of your throat behind the tongue, vibrates. Several throat muscles usually hold the pharynx open while you’re awake or upright, allowing air to pass through for proper inhale and exhale. However, these muscles relax when you sleep, causing the pharynx to vibrate as it becomes more narrow. The vibrations are what’s responsible for the snoring noise made as you breathe in. The narrower your pharynx is, the more vibration there is, leading to louder snoring.
Symptoms of Snoring
Loud, noisy breathing is one of the most prominent symptoms of snoring. Besides this, you may also experience the following symptoms:
Interrupted sleep
Frequent waking during the night
Snoring while sleeping on your back
Choking or gasping for air
Mouth breathing
Daytime fatigue
7 Common Causes of Snoring
There are many factors that can contribute to snoring. Some of them include:
Getting into a Deep Sleep
When your body shifts from light to deep sleep, the muscles in the soft palate, tongue, and throat relax. This increases the chances of leading to partial airway obstruction and vibration in the throat tissues. The narrower your airway becomes, the more forceful the airflow is, intensifying the vibrations of the tissues and consequently increasing the snoring sound volume.
Mouth/ Airway Anatomy
Having a small chin, short neck, low, thick, or soft palate, and excessive throat tissues among obese people can narrow the airway, increasing the possibility of snoring. Similarly, an elongated uvula, the triangular tissue hanging from the backend of the soft palate, can obstruct airflow and increase vibration, causing snoring.
Alcohol Consumption
Consuming too much alcohol before sleeping relaxes the throat muscles. This can reduce natural defenses, preventing your airway from being obstructed and contributing to snoring.
Nasal Problems
Those experiencing chronic nasal congestion from allergic rhinitis or a deviated nasal septum can also have snoring issues as it gets in the way of normal airflow.
Sleep Deprivation
Poor sleep quality and the lack thereof can relax throat muscles, potentially exacerbating snoring.
Sleep Position
Certain sleeping positions also contribute to snoring. You are more likely to snore when you sleep on your back since the gravitational force on the throat tends to narrow the airway.
Risk Factors
Gender
Snoring is more common in men than women, and have a higher chance of developing sleep apnea.
Weight
People who are overweight or obese are prone to snoring since the fatty tissues surrounding the throat tend to obstruct the airway.
Family History
When family members are known to have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and loudly snore, then your snoring could be a genetic predisposition.
Effects of Snoring
While snoring is typically harmless, it can impact one’s daily life and well-being. Aside from disturbing a sleeping partner, snoring, in the long run, can lead to many other health complications, including:
Daytime sleepiness
Frequent frustration or anger
Difficulty concentrating
Increased risk of high blood pressure, heart conditions, and stroke
Contributes to accidents due to compromised cognitive function
Triggers behavioral issues, such as aggression or learning problems (Especially among children with OSA)
Lack of sleep
Difference Between Snoring and Sleep Apnea
People commonly mistake snoring for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Snoring is simply the sound caused by vibrations in the airway during sleep while OSA is a more serious condition where your airway becomes partially or completely blocked, causing you to stop breathing.
In cases of OSA, your brain intervenes by briefly waking you up to restore normal breathing, often without you realizing it. These outcomes of sleep apnea limit the ability to get a restful, deep, and healthy sleep. Over time, OSA can cause complications that may affect quality of life. Thankfully, this condition is often very manageable, especially with close adherence to prescribed treatments.
Snoring can be accompanied by symptoms that cause restless sleep. However, anyone experiencing shortness of breath (dyspnea), nocturnal chest pain, excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, a sore throat upon waking up, loss of concentration, or high blood pressure may have to get checked for sleep apnea.
While loud snoring is a primary sign of sleep apnea, there is a chance your snoring can be caused by other reasons. Children who have sleep apnea may experience poor attention span, subpar, subpar school performance, and behavioral problems.
When To See a Doctor
If you think snoring symptoms or sleep apnea is affecting the quality of your life or preventing you from having a deep, restful sleep, it is important to seek treatment.
Only your doctor will be able to determine why do people snore, whether it’s because you’re experiencing sleep apnea or other factors that cause your pharynx to narrow vibrate. They’ll also be able to recommend snoring treatment options accordingly.
While mild snoring is often harmless, loud snoring or untreated sleep apnea can affect sleep quality. It may also be directly tied to an increased risk in your cardiovascular and metabolic health. The only way to identify your exact condition and understand how to stop snoring is to get a proper diagnosis.
How is Snoring Diagnosed
Very often, the sleeping partner will be able to confirm the occurrence of your snoring. During a consultation, your doctor will ask you and your partner questions related to snoring or certain symptoms, such as:
How often do you snore?
What does your snoring sound like?
Do you feel rested during the day?
Doctors may also ask you to accomplish any of the following tests to support their diagnosis.
Imaging tests
Your healthcare provider will assess your medical history. They will also conduct a physical exam to check for possible reasons that block your airways, which may include chronic nasal congestion due to rhinitis or sinusitis, a deviated septum, or swollen tonsils. They may request imaging tests like an X-ray, MRI scan, or CT scan to get a closer look or accurate view of the condition in your airways.
Sleep study
If your doctor suspects symptoms of sleep apnea, they will most likely recommend you undergo a sleep study (polysomnography), whether at home or at night in a sleep center.
Sleep study helps evaluate:
Brain wave activity.
Breathing patterns, including any periods when you stop breathing or gasp for air.
Heart rate and oxygen levels.
Movements during sleep or tossing and turning.
Sleep cycles and the occurrence of snoring.
The tests will give your healthcare provider a better idea of the main cause of your snoring condition, allowing them to suggest effective treatment options that will boost overall health and improve sleep quality.
How to Stop Snoring?
Today, there are many different snoring treatment options. Your doctor will decide which is right for you based on many factors, such as the severity of your snoring, your health history, and your personal preferences.
Non-surgical Treatment Options
Your doctor will recommend nonsurgical treatment options as the first line of treatment. This includes:
Lifestyle changes such as changing your sleep position, limiting alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Cold and allergy medications may relieve nasal congestion, enabling you to breathe easily, therefore reducing the possibility of snoring.
Nasal strips (flexible bands that stick to the outside of your nose) can be worn at night to keep the nasal passages open, reduce chances of vibrations, and thereby snoring.
Oral appliances like a mouthguard when you sleep can align your jaw in the proper position so air can flow freely. This is different from the mouthguards used for sports.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgical treatments are only recommended for severe snoring issues and in situations where the other lifestyle changes have not been effective. The goal of surgical treatment options is to remove excess tissue or correct a structural issue (like a deviated septum).
Surgical treatments may include:
Laser-assisted uvulopalatoplasty (LAUP) reduces tissue in your soft palate and improves airflow.
Somnoplasty® or ablation therapy is a technique that incorporates radiofrequency energy to shrink excess tissue in your soft palate and tongue.
Septoplasty is recommended if you have a deviated septum. It improves airflow through your nose by reshaping the cartilage and bone.
Tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy, where excess tissue is removed from either the back of your throat (tonsillectomy) or the back of your nose (adenoidectomy.)
For snoring accompanied by sleep apnea, your doctor may suggest oral appliances, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), and upper airway surgery.
Only your doctor or healthcare provider will be able to diagnose the condition accurately and suggest the best way to stop snoring and improve your quality of life.
15 Natural Remedies to Reduce or Prevent Snoring
There are many lifestyle changes you can make to stop snoring immediately and prevent them in the long run. Some of them include:
Change Your Sleep Position: Sleeping on your side can prevent the tongue and soft tissues from blocking your airway. It is one of the most effective snoring natural remedies to improve the quality of sleep.
Elevate Your Head While Sleeping: Use an adjustable bed or extra pillows to raise your head slightly, which can reduce airway obstruction.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight around the neck can lessen the pressure on the airway and reduce snoring.
Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives: These relax the muscles in your throat, increasing the risk of snoring.
Quit Smoking: Smoking irritates and inflames the airways, making snoring more likely.
Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can thicken mucus in your throat, worsening snoring.
Practice Good Sleep Hygiene: Create a consistent sleep routine to improve the quality of sleep.
Keep Nasal Passages Clear: Use saline sprays, neti pots, or nasal strips to open up nasal passages.
Use a Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can reduce nasal and throat irritation.
Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Eating large or spicy meals close to bedtime can exacerbate snoring.
Strengthen Throat Muscles: Exercises like singing or specific mouth and throat exercises can tone these muscles and reduce snoring.
Use Essential Oils: Some people find relief using oils like peppermint or eucalyptus to clear nasal passages.
Try Anti-Snoring Mouthpieces: Devices like mandibular advancement splints can help keep the airway open.
Reduce Allergens in the Bedroom: Clean and hypoallergenic mattresses and bedding help minimize irritants that contribute to snoring.
Improve Your Sleeping Environment: Ensure your bedroom is comfortable and quiet, allowing you to fall and stay asleep.
Manage Snoring With Our Sleep Doctors
Our sleep doctors specialize in diagnosing and treating snoring and related conditions like sleep apnea. With personalized care and advanced solutions, we’ll help you achieve restful, uninterrupted sleep.
Whether it’s mild snoring or something more serious, we’re here to guide you toward better health and peaceful nights.
Take the first step toward quieter, restorative sleep - schedule a consultation with our experts today!